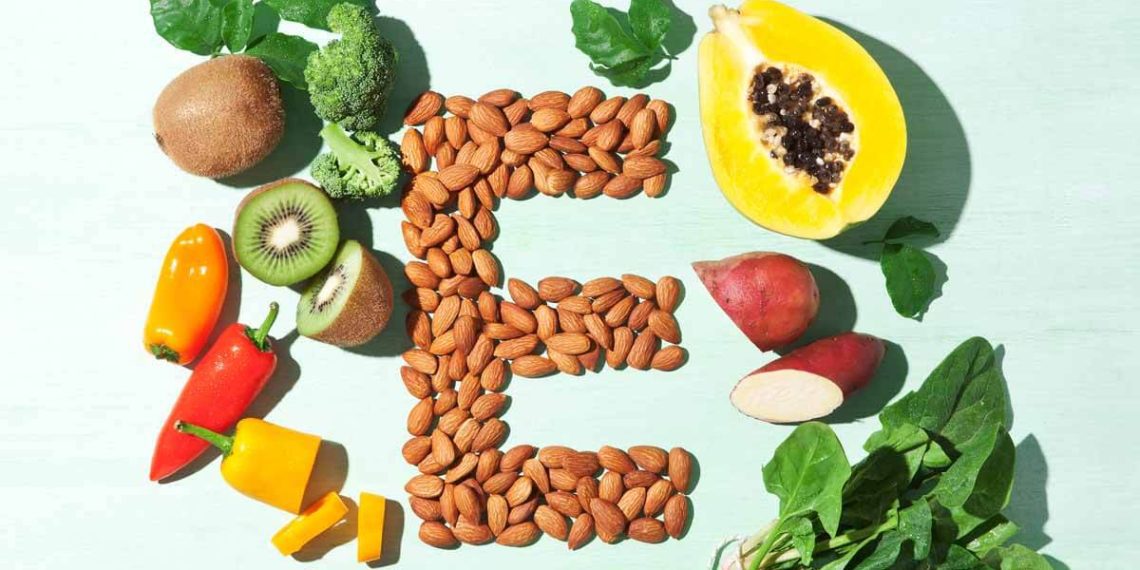Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources – Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that offers numerous health benefits, including protecting the body against free radicals, reducing inflammation, and supporting the immune system. In this article, we will explore the health benefits of vitamin E, its recommended daily intake, and the best food sources of this essential nutrient.
Table of Contents
What is Vitamin E?
Vitamin E is a group of eight fat-soluble antioxidants that play an important role in protecting the body against oxidative stress. These antioxidants include four tocopherols (alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-tocopherol) and four tocotrienols (alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-tocotrienol). Alpha-tocopherol is the most active form of vitamin E in the human body and is the form most commonly found in supplements and fortified foods.
Health Benefits of Vitamin E
- Protects Against Free Radicals
Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant, protecting the body against the harmful effects of free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Reduces Inflammation
Vitamin E has anti-inflammatory properties that may help to reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to a variety of health problems, including heart disease, cancer, and arthritis.
- Supports the Immune System
Vitamin E plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy immune system. It helps to protect immune cells from oxidative stress and supports the production of antibodies, which are essential for fighting infections.
- May Lower the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Research has suggested that vitamin E may help to lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin E
The recommended daily intake of vitamin E varies depending on age and gender. The following table shows the recommended daily intake of vitamin E for different age groups:
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin E |
|---|---|
| 0-6 months | 4 mg (6 IU) |
| 7-12 months | 5 mg (7.5 IU) |
| 1-3 years | 6 mg (9 IU) |
| 4-8 years | 7 mg (10.4 IU) |
| 9-13 years | 11 mg (16.4 IU) |
| 14+ years | 15 mg (22.4 IU) |
Pregnant and breastfeeding women may require higher amounts of vitamin E. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Best Food Sources of Vitamin E
Vitamin E is found naturally in a variety of foods, including:
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, sunflower seeds, hazelnuts)
- Vegetable oils (sunflower oil, safflower oil, wheat germ oil)
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, broccoli, Swiss chard)
- Fortified cereals and other fortified foods (bread, milk, yogurt)
It’s important to note that vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin, which means that it is better absorbed when consumed with fat-containing foods. Therefore, it’s recommended to consume vitamin E-rich foods with a source of healthy fat, such as avocado or olive oil.
Related: wellhealthorganic.com:health-hazards-of-prolonged-sitting
Conclusion
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that offers numerous health benefits, including protecting the body against free radicals, reducing inflammation, and supporting the immune system. The recommended daily intake of vitamin E varies depending on age and gender, and it can be obtained from a variety of foods, including nuts and seeds, vegetable oils, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals. By incorporating these foods into your diet by Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources, you can ensure that you are getting the recommended daily amount of vitamin E and supporting your overall health and wellbeing.
When it comes to optimizing your health through vitamin E consumption, it’s important to prioritize nutrient-dense whole foods rather than relying on supplements alone. While vitamin E supplements can be useful in certain situations, such as for individuals with a diagnosed deficiency or those who have trouble absorbing nutrients from food, it’s always best to focus on obtaining vitamins and minerals through a well-rounded diet.
In addition to consuming vitamin E-rich foods, there are other lifestyle factors that can support your overall health and wellbeing. These include regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. By making small changes to your daily routine and prioritizing healthy habits, you can support your body’s natural ability to fight disease and stay healthy.